Uninterruptible Power Supply: Ensuring Continuous Power for Modern Life
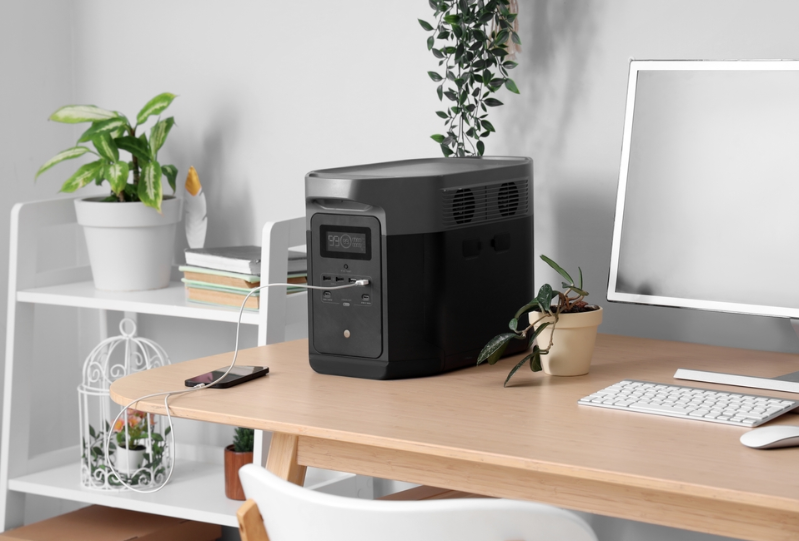
In today’s digital age, power reliability is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether in homes, offices, data centers, or healthcare facilities, an unexpected power outage can cause severe disruption. This is where an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) comes into play. Designed to provide continuous power during outages or voltage fluctuations, a UPS is a critical component for protecting sensitive equipment and maintaining business continuity.
What is an Uninterruptible Power Supply?
An uninterruptible power supply is an electrical device that offers emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically the main utility, fails. Unlike standby generators that take time to start, a UPS provides near-instantaneous protection from power interruptions. It serves as a buffer between your equipment and the power source, ensuring devices remain operational even during short-term or sudden power outages.
See also: How to Troubleshoot Wiring Issues with the Wire Landing Board Saving You Hours on Site
How Does a UPS Work?
A UPS system typically consists of three core components:
- Rectifier/Charger: Converts incoming AC (alternating current) power into DC (direct current) to charge the internal battery.
- Battery: Stores energy for immediate use during a power failure.
- Inverter: Converts DC back into AC to supply your devices with uninterrupted power.
When the primary power source is stable, the UPS charges its battery. Upon detecting a disruption, the system instantly switches to battery power, maintaining a consistent supply to connected equipment.
Types of Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems
There are several types of UPS systems, each suited for specific applications:
- Offline/Standby UPS: Provides basic protection and switches to battery power during outages. Ideal for personal computers or small office devices.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Offers automatic voltage regulation to handle minor fluctuations without switching to battery. Perfect for small business servers or network equipment.
- Online/Double Conversion UPS: Continuously supplies clean power by converting AC to DC and back to AC. This is the most reliable type for data centers, hospitals, and critical systems requiring zero downtime.
Benefits of Using a UPS
Investing in an uninterruptible power supply provides several advantages:
- Prevents Data Loss: Protects computers, servers, and storage devices from sudden shutdowns.
- Maintains Business Continuity: Critical systems, such as security or medical equipment, remain operational during outages.
- Voltage Regulation: Reduces the risk of damage caused by voltage spikes, sags, or surges.
- Protects Hardware: Prolongs the life of sensitive equipment by providing a stable power supply.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your essential devices will remain operational even during blackouts reduces stress for businesses and homeowners alike.
Applications of UPS Systems
UPS systems are versatile and used in numerous industries:
- Data Centers: Ensures uninterrupted server operation, preventing data loss and downtime.
- Healthcare: Supports life-saving equipment like ventilators and monitoring devices.
- Telecommunications: Maintains continuous operation of critical communication networks.
- Industrial Automation: Keeps manufacturing equipment running smoothly during power disturbances.
- Home Offices: Protects personal computers and networking devices from unexpected outages.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a UPS
Selecting the right UPS requires careful evaluation of several factors:
- Capacity: Measured in VA (volt-amperes) or kVA, the UPS must support the total load of connected devices.
- Runtime: Determine how long the UPS can supply power during an outage.
- Form Factor: Tower or rack-mounted, depending on available space.
- Battery Type: Sealed lead-acid, lithium-ion, or other advanced technologies.
- Efficiency and Features: Look for advanced features like automatic voltage regulation, LCD display, network management, and alerts.
Maintenance Tips for a UPS
To ensure longevity and reliability of your UPS:
- Regularly check battery health and replace as recommended.
- Keep the UPS in a cool, dry environment.
- Clean dust and debris from vents and fans.
- Perform periodic load tests to verify performance.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for firmware updates and servicing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How long does a UPS battery last?
A UPS battery typically lasts between 3 to 5 years, depending on usage, environmental conditions, and battery type.
Q2: Can a UPS power all home appliances?
No. UPS systems are designed for sensitive electronics. High-power appliances like air conditioners or refrigerators require specialized solutions.
Q3: Does a UPS protect against lightning strikes?
A UPS can protect against minor voltage surges, but it is not a replacement for surge protectors or lightning protection systems.
Q4: What is the difference between UPS and a generator?
A UPS provides instantaneous backup for short durations, while generators supply long-term backup but take time to start.
Q5: Can I use a UPS with solar power systems?
Yes, many UPS systems can integrate with solar inverters to ensure continuous power supply.
Conclusion
An uninterruptible power supply is more than just a convenience—it is a critical safeguard for modern life. From preventing data loss and hardware damage to ensuring business continuity, a UPS is indispensable in today’s power-dependent world. By selecting the right type, maintaining it properly, and understanding its capabilities, you can enjoy uninterrupted operations and peace of mind, no matter what challenges your power grid may face.